Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis in a female with ovarian tumor: A case report in Viet Nam
- Hung Vuong Hospital, No. 128, Hong Bang Str., Ward 12, District 5, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
- Pham Ngoc Thach University of Medicine, No. 2, Duong Quang Trung St., Ward 12, District 10, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
- Cho Ray Hospital, No. 201B, Nguyen Chi Thanh Str., Ward 12, District 5, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
- Nguyen Tat Thanh University, No. 300A, Nguyen Tat Thanh Str., Ward 13, District 4, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
Abstract
Background: Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (anti-NMDAR) encephalitis is a rare form of autoimmune encephalitis with no established consensus on treatment. Although some reports have recommended surgical intervention combined with immunotherapy, outcomes have been inconsistent. This report presents a unique case of anti-NMDAR encephalitis in a 19-year-old female with an ovarian tumor treated with plasmapheresis and systemic corticosteroids.
Case report: The patient initially presented with mild fever before hospital admission, which then progressed to delirium, agitation, and unconsciousness. Indirect immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) testing revealed positive anti-NMDAR immunoglobulin G (IgG) in both serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples. Pelvic computed tomography (CT) imaging identified a 29 × 21 mm tumor in the left ovary. Due to the patient’s critical condition, no surgery was performed. Instead, she received systemic corticosteroids and underwent seven sessions of plasmapheresis. Within 23 days of treatment, the patient’s anti-NMDAR IgG became undetectable, and her clinical status improved significantly. At a recent re-examination, she demonstrated good recovery.
Conclusions: This case underscores a non-surgical management approach to anti-NMDAR encephalitis with a favorable outcome. Although the absence of histopathological confirmation limits the interpretation, the patient’s recovery following immunotherapy alone raises important questions about the origin of autoantibody production. Further research is needed to elucidate potential tumor-independent mechanisms underlying anti-NMDAR encephalitis and to guide individualized treatment approaches, particularly in settings where tumor resection may not be feasible.
Introduction
NMDAR encephalitis is a rare form of encephalitis but is relatively common within the autoimmune encephalitis category. Its pathophysiological mechanism remains under debate, with the prevailing hypothesis pointing to autoantibodies targeting N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the brain1. The presence of an ovarian teratoma is often implicated as a primary source of these autoantibodies2; because the tumor contains multiple highly differentiated cell lines, it produces specific circulating autoantibodies3. However, alternative mechanisms—including passive diffusion of autoantibodies across the blood–brain barrier or intrathecal autoantibody production—have also been proposed4.
Numerous findings support the tumor-related autoantibody production hypothesis. Current recommendations for anti-NMDAR encephalitis emphasize immunotherapies and tumor resection, as the combined approach appears to improve patient outcomes1. Nevertheless, treatment outcomes remain uncertain in cases where surgical intervention is not performed. In this case report, we describe the diagnosis and treatment of NMDAR encephalitis in a female patient who underwent no surgical intervention for her ovarian tumor.
Case Presentation
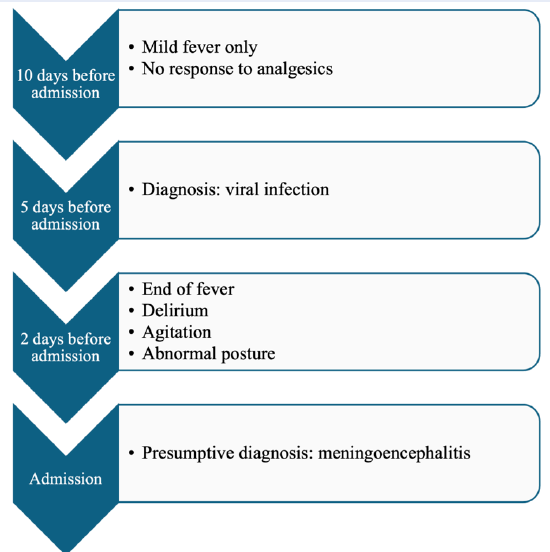
A 19-year-old patient was admitted due to loss of consciousness. The chronological progression of symptoms is outlined in Figure 1. On examination, the Glasgow Coma Scale was 10 points (eye opening 4, motor response 5, verbal response 1). The patient’s blood pressure was 120/89 mmHg, and the heart rate was 112 bpm. She denied any respiratory, gastrointestinal, or urogenital infections. There was no history of trauma, and no bruising or purpura were observed on the skin. Neurological examination showed pupils measuring 3 mm with intact light reflexes; neck stiffness and Babinski signs were negative. A bedside glucose test revealed 131 mg/dL. Head computed tomography (CT) revealed no intracranial lesions. Electroencephalography showed bifocal slow-wave activity. Meningoencephalitis was the primary diagnosis, with microvascular stroke considered as a differential diagnosis.
Laboratory results of the patient on admission day
|
Total blood count |
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis | ||
|
Red blood cell |
4.44 (T/L) |
CSF glucose |
65 (mg/dL) |
|
Hemoglobin |
132 (g/L) |
CSF lactate |
16.8 (mg/dL) |
|
White blood cell |
12.09 (G/L) |
CSF protein |
27.2 (mg/dL) |
|
Neutrophil count |
10.41 (G/L) |
CSF-to-blood glucose ratio |
0.677 |
|
Lymphocyte count |
0.84 (G/L) |
ADA |
0.3 (U/L) |
|
Monocyte count |
0.67 (G/L) | ||
|
Eosinophil count |
0.03 (G/L) | ||
|
Basophil count |
0.02 (G/L) | ||
|
Platelet count |
301 (G/L) | ||
|
Immunological test | |||
|
Anti ds-DNA |
4.58 (IU/ml) | ||
|
Anti-Sm |
0.29 (U/ml) | ||
|
Cardiolipin IgG |
<2.0 (U/ml) | ||
|
Cardiolipin IgM |
2.5 (U/ml) | ||
|
fT3 |
2.06 (pg/ml) | ||
|
fT4 |
14 (pg/ml) | ||
|
TSH |
0.49 (mIU/L) | ||
|
ANA |
Negative | ||
|
Blood IFT for autoimmune encephalitis |
CSF IFT for autoimmune encephalitis | ||
|
GABA-RB1/B2 |
Negative |
GABA-RB1/B2 |
Negative |
|
LGI1 |
Negative |
LGI1 |
Negative |
|
CASPR2 |
Negative |
CASPR2 |
Negative |
|
DPPX |
Negative |
DPPX |
Negative |
|
AMPA-R1/R2 |
Negative |
AMPA-R1/R2 |
Negative |
|
NMDAR |
Positive |
NMDAR |
Positive |
Diagnostic Workup
A complete blood count was performed to screen for infection and adverse treatment events. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) aspiration yielded no bacterial or fungal growth; blood culture findings were consistent with polymerase chain reaction assays for M. tuberculosis or Herpes simplex virus. No evidence of microvascular stroke was detected on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Thus, both infectious meningoencephalitis and stroke were deemed unlikely. Detailed laboratory findings are presented in
The diagnostic focus then shifted toward autoimmune etiology. Serum autoantibody tests, including anti-ds-DNA, anti-SM, and anti-phospholipid, were negative. However, anti-NMDAR IgG was positive in both serum (screening at 1:10) and CSF (screening at 1:1), confirming NMDAR encephalitis. Concurrently, pelvic CT revealed a 29 × 21 mm fluid-density mass in the left ovary. Surgery was deemed too high risk due to the patient’s critical status, and thus histopathologic features of the tumor could not be determined.
According to institutional policy, ethical approval for this single anonymized case report was not required; however, written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s legal guardian for both treatment and publication, including use of anonymized data.
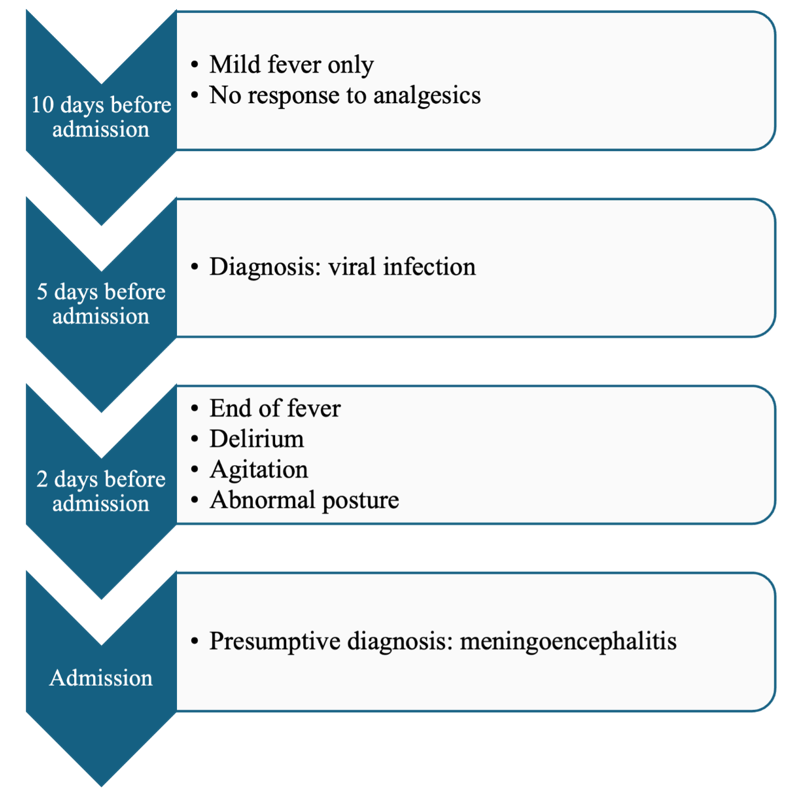
Symtomp presentation in chronological order.
Treatment and Outcome
Upon admission, the patient was unable to communicate effectively due to agitation and delirium. Treatment comprised intravenous immunoglobulin, midazolam, and high-dose methylprednisolone, although symptom progression was only slowly alleviated. Plasmapheresis was then initiated; during the procedure, purpura appeared on both limbs but resolved rapidly. After seven plasmapheresis sessions, the patient recovered consciousness and displayed neurological improvement, including the ability to breathe spontaneously and tolerate oral nutrition. She experienced a few intermittent catatonic episodes. Following 23 days of treatment, she was discharged with marked clinical improvement (
Summary of treatment regimen
|
Therapy |
Agent/Dose |
Duration/ Frequency |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IV Immunoglobulin |
0.4 g/kg/day |
5 days |
No significant improvement |
|
Corticosteroid |
Methyl prednisolone 1g/day |
5 days |
High-dose pulse therapy |
|
Plasmapheresis |
Single volume exchange |
Every other day, 7 sessions total |
Significant clinical improvement |
|
Symptomatic (sedation) |
Midazolam infusion |
PRN |
Used during agitation |
Discussion
Since first reported in 2008, anti-NMDAR encephalitis has become one of the most common forms of autoimmune encephalitis, particularly in young females. It involves autoantibodies against the GluN1 subunit of NMDA receptors, manifesting a broad spectrum of neuropsychiatric symptoms. Multiple investigations have documented its association with ovarian teratomas, which may harbor neural tissue and elicit an immune response. Comprehensive tumor screening is therefore standard in the diagnostic process1, 2, 3.
This patient presented similarly to previously documented cases, with a viral-like prodrome, rapid onset of neuropsychiatric manifestations, anti-NMDAR antibodies in both serum and CSF, and no evident infectious or structural etiology. Pelvic CT identified a cystic lesion in the left ovary, consistent with a tumor, although the patient’s unstable status precluded surgical resection and histopathological confirmation. Consequently, the direct role of the lesion in antibody production cannot be definitively established. Future cases should undergo histological evaluation when clinically feasible to refine diagnostic accuracy.
Despite the unresolved tumor status, the patient responded well to high-dose corticosteroids and plasmapheresis. Because initial intravenous immunoglobulin therapy did not prompt significant improvement, plasma exchange was introduced, consistent with current first-line therapeutic recommendations1, 5. Rituximab was not employed due to limited availability and its usual role as a second-line agent. Other reports in resource-limited settings describe favorable outcomes using a steroid–plasmapheresis combination when surgical or biologic options are not viable6, 7.
Symptom resolution and seroconversion (loss of anti-NMDAR IgG) despite retaining the ovarian lesion raise important questions regarding underlying antibody production mechanisms. Despite a plausible tumor relationship, potential alternatives include transient tumor-mediated autoimmunity, intrathecal synthesis of antibodies independent of peripheral triggers4, or post-infectious immune processes8, 9, 10. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis has additionally been observed in males, children, and adults without detectable tumors11, 12, 13, indicating that non-paraneoplastic mechanisms may also be involved.
At six-month follow-up, the patient demonstrated complete neurological and psychiatric recovery with negative serum anti-NMDAR IgG. However, imaging showed persistence of the ovarian lesion. Given the higher relapse risk in patients whose tumors remain in situ5, a structured surveillance plan was initiated, involving quarterly neuropsychiatric assessments and antibody monitoring for one year, then biannual evaluations. Surgical management will be reconsidered if there is any sign of progressive lesion growth or clinical relapse. Mental health screening remains a priority, given the potential for subclinical recurrence arising from residual low-titer antibodies14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20.
This case report demonstrates a rare example of successful non-surgical management of anti-NMDAR encephalitis, with comprehensive diagnostic, therapeutic, and follow-up protocols. Strengths include reliable exclusion of alternate diagnoses, a clear treatment rationale, and applicability to resource-limited settings.
Nonetheless, several limitations must be acknowledged. Without histopathological data on the ovarian lesion, definitive conclusions regarding the source of antibody production cannot be made. As a single case, its findings cannot be universally applied. Additionally, while the patient remained relapse-free at six months, longer-term outcomes remain unknown, and the absence of serial CSF antibody titers impedes more detailed immunological insight.
Conclusion
This case underscores a non-surgical management pathway for anti-NMDAR encephalitis that yielded a favorable outcome. Although the absence of histopathological confirmation limits the interpretation, the patient’s recovery following immunotherapy alone prompts critical questions regarding the source of autoantibody production. Further investigations are warranted to elucidate tumor-independent mechanisms in anti-NMDAR encephalitis and to guide individualized treatment strategies—particularly in resource-limited settings, where tumor resection may not always be feasible.
Abbreviations
Anti-NMDAR: Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor IFA: indirect immunofluorescence antibody; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; CT: computed tomography; IgG: immunoglobin G.
Acknowledgments
None.
Author’s contributions
TM and NT prepared the manuscript, AT analyzed the case, DT, QH edited the entire manuscript and gave advice on the case, KT, TV, NK provided advice on the case. NT was responsible for editing the whole manuscript, especially advising on issues relating to management and implementation. All authors edited and approved the contents of the submitted manuscript.
Funding
None.
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s mother for publication of this Case Report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
The authors declare that they have not used generative AI (a type of artificial intelligence technology that can produce various types of content including text, imagery, audio and synthetic data. Examples include ChatGPT, NovelAI, Jasper AI, Rytr AI, DALL-E, etc) and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process before submission.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.

