latest articles
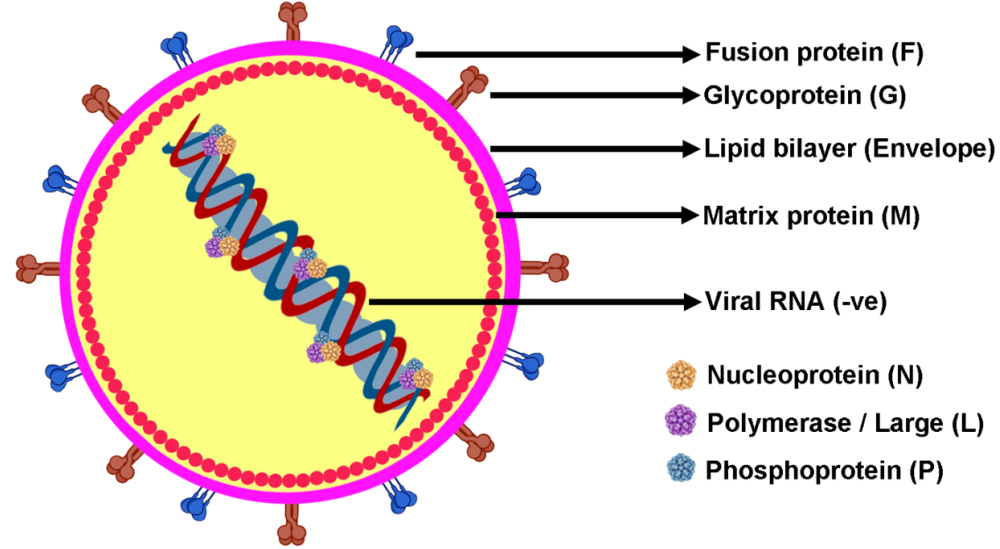
Nipah Virus: Transmission Dynamics of a Zoonotic Outbreak and Therapeutic Challenges
by Kiran
V.,
Girigoswami
K.,
Girigoswami
A.
Summary: Nipah virus (NiV) is a deadly zoonotic virus that has caused multiple outbreaks since it was first identified in Malaysia in 1998. It is primarily transmitted by fruit bats and can spread among humans, leading to severe neurological and respiratory complications. With fatality rates ranging from 40% to 75%, NiV poses a serious public health threat, and there are currently no approved treatments or vaccines. The virus enters human cells via ephrin-B2 and ephrin-B3 receptors, causing extensive harm while evading the immune system, which complicates treatment efforts. Environmental changes, including deforestation and increased human–wildlife contact, have heightened the likelihood of NiV outbreaks. Preventing future outbreaks necessitates early detection, strict biosecurity measures, and concerted global efforts to develop antiviral therapies and vaccines. This review comprehensively examines NiV's virology, transmission dynamics, clinical manifestations, and the latest advances in therapeutic care, encompassing One Health strategies and preventive measures.
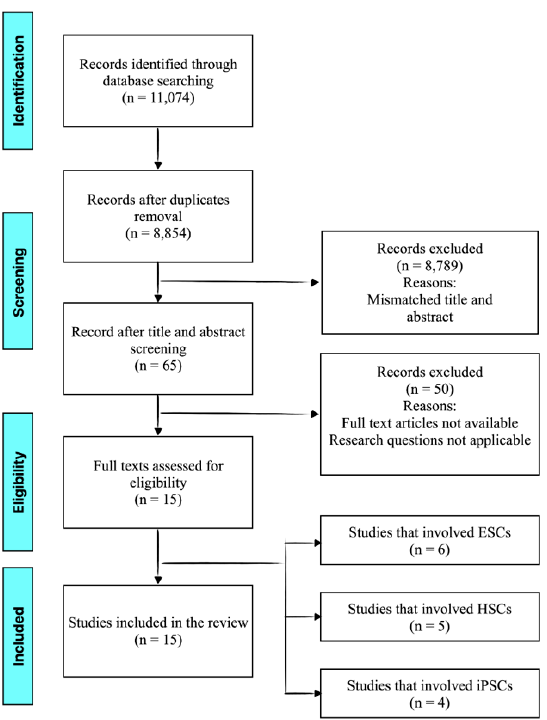
Unraveling Common Stem Cell Sources and Key Reporting Parameters in Studies Related to Stem Cell-Derived Red Blood Cells: A Review
by Noordin
S.,
Al-Amoudi
B.,
Mohamed
R.,
Aziz
M.,
Noor
S.,
Zabidi
M.
Summary: Blood transfusions are essential for maintaining oxygen delivery to tissues in cases of severe blood loss. However, challenges such as limited donor availability, short storage lifespans, blood-type incompatibility, and infection risks necessitate alternative solutions. Stem cell-derived red blood cell (RBC) substitutes offer a promising approach to address these limitations. Multiple stem cell sources, including embryonic stem cells (ESCs), hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have been explored for RBC generation. ESCs pose ethical and immunogenicity concerns; HSCs exhibit limited proliferation potential and variable outcomes; iPSCs face safety, standardization, and scalability challenges for RBC generation. Despite significant research in this area, no comprehensive mapping of the evidence exists. This scoping review aims to systematically map the literature on stem cell-derived RBC substitutes and identify key reported parameters.
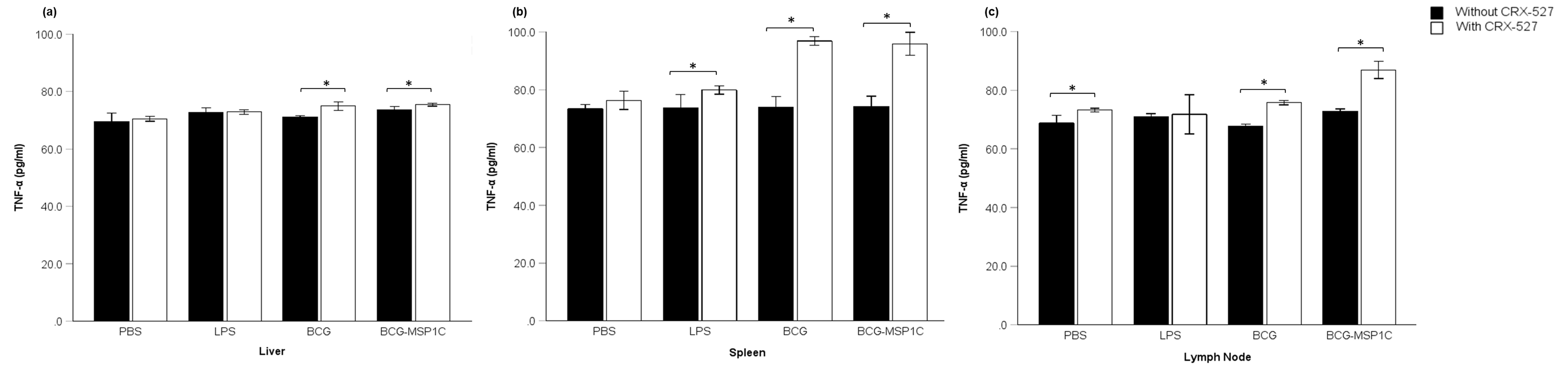
TLR4 Agonist CRX-527 Modulates Intracellular and Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Lymphoid Tissues of BCG-MSP1C-Immunized Mice
by Hanifi
N.,
Zakaria
N.,
Suppian
R.
Summary: Due to the complexity of the malaria parasite’s life cycle, together with the limited knowledge of its intricate immunological response, this study was conducted. This study aims to evaluate the ability of a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist, CRX-527, to enhance the production of intracellular and inflammatory cytokines in lymphocyte-derived tissues of malaria vaccine candidates.
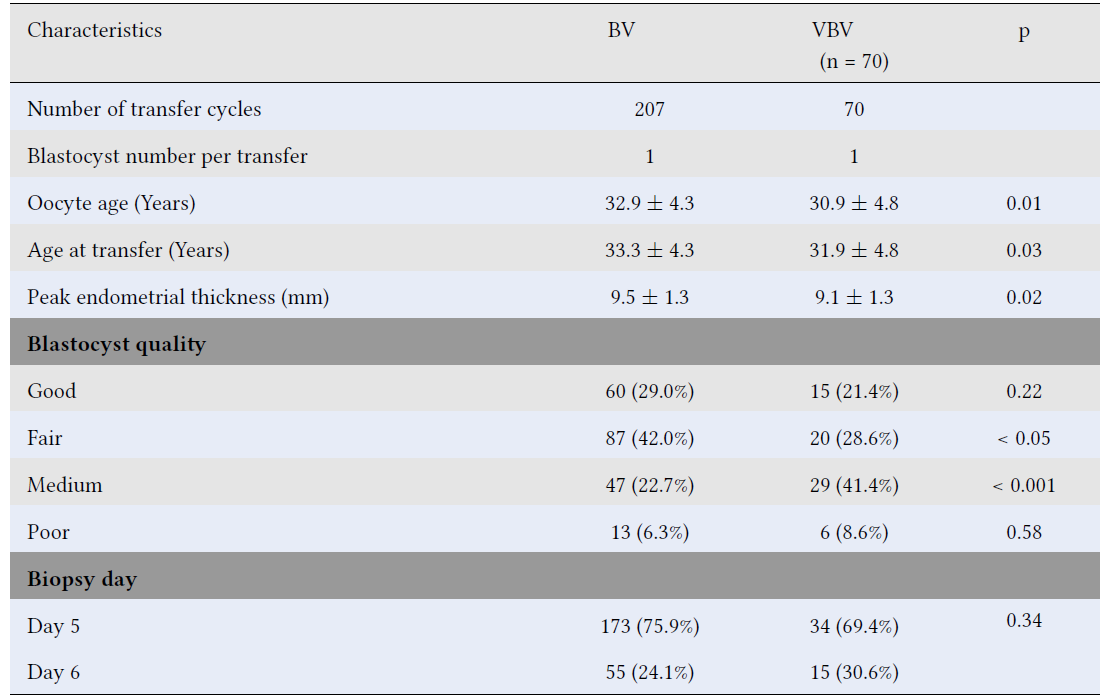
Double Vitrification-Warming Cycles Reduce Live Birth Rates in Single Euploid Blastocyst Transfers: A Retrospective Cohort Study
by Tran Thi
T.,
Le Thi Thuy
D.,
Nguyen Dinh
T.,
Nguyen Hong
P.,
Pham Van
L.,
Nguyen Ha
T.,
Nguyen Thanh
L.,
Ngo Van
T.
Summary: To evaluate the impact of blastocysts biopsied once and vitrified twice on clinical outcomes.
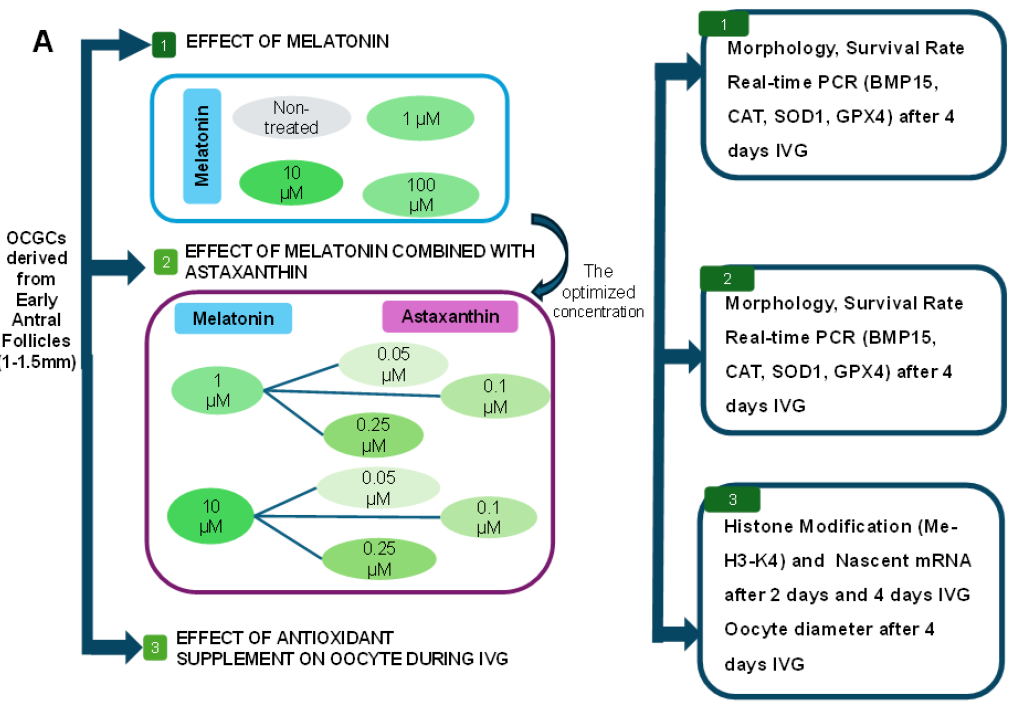
Impact of Antioxidant Supplementation on In Vitro Growth of Porcine Oocytes Derived from Early Antral Follicles
by Chi Thien
L.,
Truc Phuong
L., D.,
Duy
P.,-T.,
Boi Linh
N., L.,
Anh My
L., B.,
Su Pham
C., D.,
Thao Vy
N., N.,
Van Anh
T., P.,
Nhat Thinh
N.,
Van Thuan
N.,
Bui
H.-T.
Summary: Oxidative stress (OS), a key factor impairing oocyte developmental competence, poses a major challenge in in vitro growth (IVG) systems. While antioxidant supplementation can mitigate OS-driven deficits, combining agents with complementary mechanisms—such as melatonin (Mela) and astaxanthin (Asta)—may offer synergistic benefits. This study evaluates the effects of Mela and Asta, individually and in combination, on oocyte quality, gene expression, and epigenetic markers during IVG.
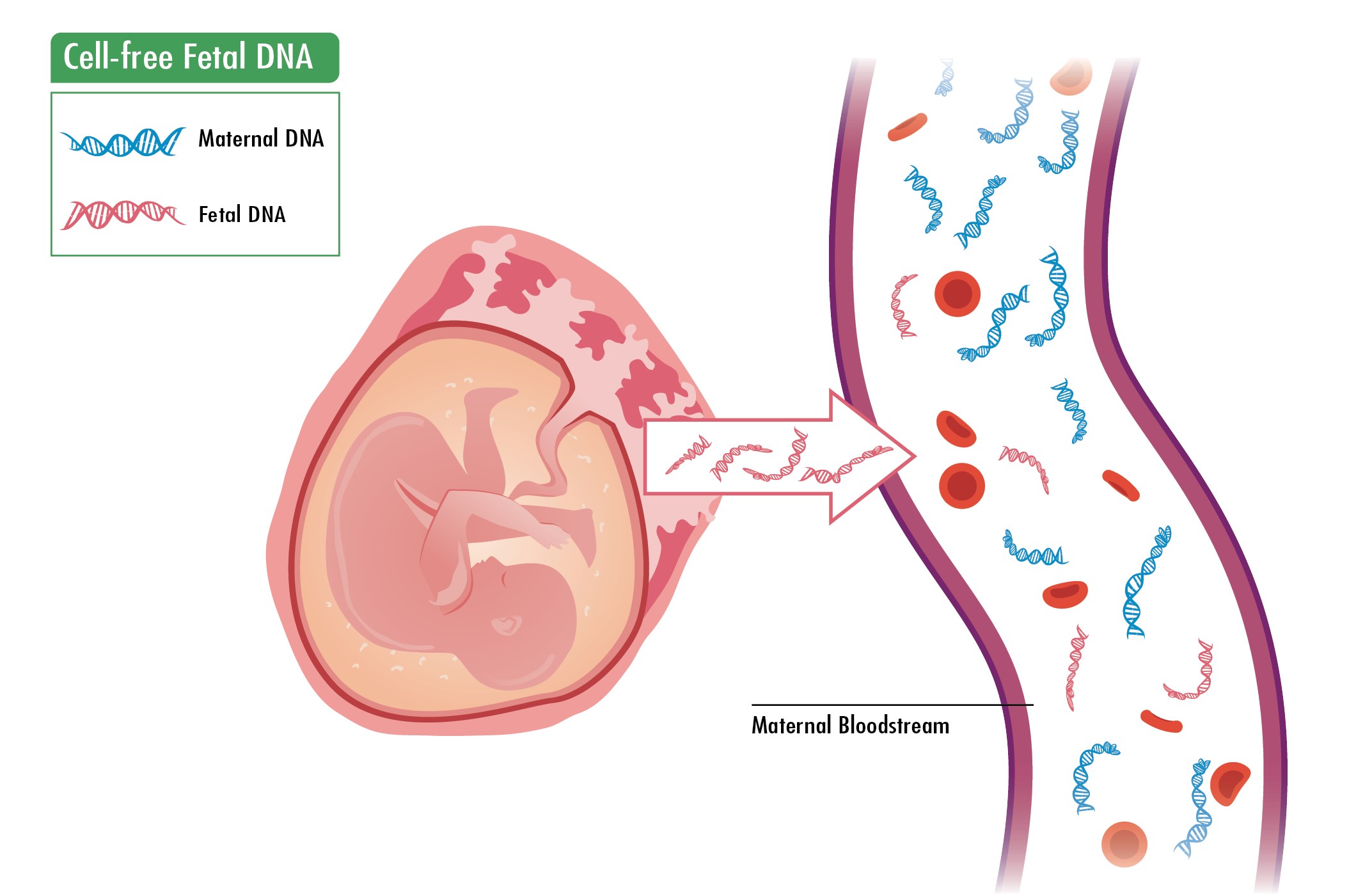
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing: Advances, Applications, and Limitations in Prenatal Screening
by Yu
T.,
Xu
X.,
Wei
Q.
Summary: Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a prenatal screening technology based on the analysis of cell-free fetal DNA (cfDNA) detected in maternal peripheral blood. It offers high detection efficiency for common chromosomal aneuploidies, such as trisomy 21 (T21), trisomy 18 (T18), trisomy 13 (T13), and sex chromosome aneuploidies (SCA). Additionally, NIPT has expanded to include the screening of subchromosomal microdeletions and microduplications, single-gene genetic diseases, and has even demonstrated certain diagnostic value for placental-derived complications during pregnancy. However, some of the problems it presents, such as technical limitations and ethical or psychological issues, cannot be overlooked. This article reviews the advancements and limitations of NIPT in prenatal screening.
Dysregulation of miR-124-3p and STAT3 in Hypothyroidism: Implications for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Biomarkers
by Kumar
A.,
Kanagarajan
P.,
Parambath
A.,
Sekar
D.
Summary: Hypothyroidism is a clinical condition caused by decreased thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) levels, affecting ~5% of the population. However, its molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Recent studies implicate microRNAs (miRNAs) in disease-related cellular processes. This study aimed to identify novel miRNAs associated with hypothyroidism using publicly available genomic databases, with the goal of validating one candidate miRNA and its target gene in patients to evaluate their potential as diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers.

Efficient Enrichment of Muse Cells from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Collagenase and Hypoxic Stress
by Minh Le
T.,
Bao Phan
N.,
Tuan Truong
K.,
Bich Vu
N.
Summary: Muse (multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring) cells are a pluripotent subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), characterized by their stress tolerance and significant potential in regenerative medicine. However, their low abundance poses challenges for isolation. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of severe stress conditions—including low temperature, severe hypoxia, and collagenase treatment (LHC)—in isolating Muse cells.

Potential Protection of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Oxidative Stress With Hypoxia Preconditioning and Lipopolysaccharide Exposure
by Fajri
F., M., E.,
Yuhendri
V., M.,
Elmi
E.,
Saputra
N., P., K.,
Arfianti
A.
Summary: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are among the most promising therapeutic options for degenerative diseases. However, the low viability and prolonged doubling time of MSCs during ex vivo expansion remain obstacles in their application in MSC-based therapies. MSC preconditioning has been considered a potential strategy to overcome challenges in MSC culture and to increase the therapeutic effects of MSCs. To mimic an inflammatory microenvironment and enhance stress resilience, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was combined with hypoxia preconditioning. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of hypoxia and LPS preconditioning on viability, population doubling time, and expression levels of antioxidant genes in MSCs.

Surface Display of Alpha-Toxin HlaH35LH48L on Bacillus subtilis Cells for Oral Vaccine Delivery in Mice
by Nguyen
N.,
Duong
L.,
Nguyen
A.,
Dinh
T.,
Phan
T.,
Nguyen
H.
Summary: Surface display of proteins on Bacillus subtilis has emerged as a promising strategy in vaccinology, leveraging its safety, gastrointestinal resilience, and capacity for efficient antigen presentation. Targeting Staphylococcus aureus, a pathogen reliant on alpha-toxin (Hla) for virulence, this study focuses on a detoxified variant, HlaH35LH48L, to potentially neutralize toxicity while preserving immunogenicity. We investigated B. subtilis as an oral vaccine vector to display HlaH35LH48L and elicit mucosal and systemic immune responses in mice.

Plerixafor for Stem Cell Mobilization in Autologous Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Series of Lymphoma Patients from a Northeastern Malaysian Teaching Hospital
by Zulkeflee
R.,
Hassan
M., N.,
Saidin
N., I., S.,
Akbar
N., A., N.,
Abdullah
M.,
Husin
A.,
Abdullah
A., D.,
Sidik
M. A.
Summary: In recent years, plerixafor, a CXCR4 chemokine receptor inhibitor, has emerged as a promising agent for the mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) when combined with other mobilizers such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and chemotherapy in patients with multiple myeloma and lymphoma undergoing autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (APBSCT). Our facility has recently implemented plerixafor as a specialized rescue treatment in lymphoma patients who are at risk or have experienced mobilization failure with G-CSF.

Human In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models in Angiogenesis Research: Advances and Challenges
by Razmi
M.,
Ugusman
A.,
Sulaiman
N.,
Ahmad
M.,
Abdul-Ghani
S.,
Ismail
M.,
Mohamad Anuar
N. N.
Summary: Angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation, is a complex phenomenon that plays a crucial role in various physiological and pathological processes, including embryonic development, tissue repair, vascular homeostasis, and tumor microenvironments. The utilization of human in vitro and ex vivo models to study angiogenesis is an actively investigated area that holds great promise for offering novel insights and prospects for developing methods to treat angiogenesis-related diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. Combining in vitro and ex vivo models using human samples can enhance the understanding of the complex process of angiogenesis in the human body. This integrative strategy facilitates a holistic exploration of angiogenesis, bridging the gap between simplified in vitro systems and the complexities inherent in in vivo settings, thereby augmenting the translational prospects of research outcomes for clinical applications. However, ethical constraints, inherent individual variability in human samples, challenges in obtaining tissue samples, technical issues in tissue handling, and the high cost involved are key limitations to consider.

Murine Models of Allergic Asthma: Methodological Insights into Allergen Sensitization and Challenge Protocols
by Bushra
S., M., R.,
Nurul
A. A.
Summary: Asthma represents a chronic inflammatory airway disease with a steadily increasing global prevalence in recent decades. Animal models have proven invaluable in elucidating the underlying disease mechanisms and identifying innovative therapeutic approaches. The murine model is extensively used to investigate key characteristics of allergic asthma, including airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), and airway remodeling. Classic protocols involving sensitizing and challenging animals with different types of allergens and modes of administration are major factors in inducing asthmatic features in a mouse model. The present review critically analyzes the commonly used sensitization and allergen challenge protocols for inducing acute and chronic inflammation in the airways of mouse models of asthma, emphasizing their potential in advancing therapeutic development for allergic asthma studies.

Investigating the Immunomodulatory Effects of Tieu U Hoan Herbal Preparation in a Murine Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model
by Luu
H., T., T.,
Nguyen
H. S.
Summary: Traditional medicine treatments (TMT) are widely recognized as effective complementary therapies in cancer care, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Tieu u hoan (TUH), an herbal formulation derived from TMT principles and clinical expertise, has shown promise in preclinical and clinical studies as a supportive therapy for HCC. This study investigates the immunomodulatory effects of TUH in immunodeficient nude mice engrafted with human Hep3B liver cancer cells.
Journal Collections

Covid-19 publications
Journal Supplements

Conference Abstracts
Journal Collections

Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
Special Issues

Special Issues
Journal Collections

Natural Extract
Publication Awards

The best original research articles
Editors' quote

Phuc Van Pham, Editor-in-Chief
Affiliation

Why publish with Biomedical Research and Therapy



 Biomedpress
Biomedpress





